What Is the Ocean Battery? It Could Be Crucial for Renewable Energy Storage
Published Jan. 10 2022, 10:10 a.m. ET
Renewable energy resources, such as solar and wind energy, are absolutely incredible — they're low-impact, extremely efficient, and in the long run, less expensive than non-renewables. But what happens when it's been a particularly cloudy week, or if the wind has significantly died down for a few days? That's where a new piece of technology called the Ocean Battery, from a Dutch sustainable tech company called Ocean Grazer, is intended to come into play.
"No one has resolved the global energy storage problem in a scalable, reliable, and affordable the way — up till now! Ocean Grazer offers a brilliant yet simple solution, based on existing technology, enhancing marine life along the way. Introducing: the Dutch engineers who solved one of the biggest hurdles towards a sustainable future," reads the company's press release, shortly after Ocean Grazer launched the Ocean Battery at CES 2022 on Jan. 5.
"Ocean Battery resolves a societal challenge to provide access to renewable power generation without destabilizing the power grid and meet our climate goals. The Dutch Water engineers resolved this problem in a brilliant yet simple way with a tremendous amount of creativity, innovation power and Dutch entrepreneurship," the press release continues.
Keep reading for more on this exciting new piece of technology, that could be revolutionary for the transition to cleaner means of energy.
What is the Ocean Battery?
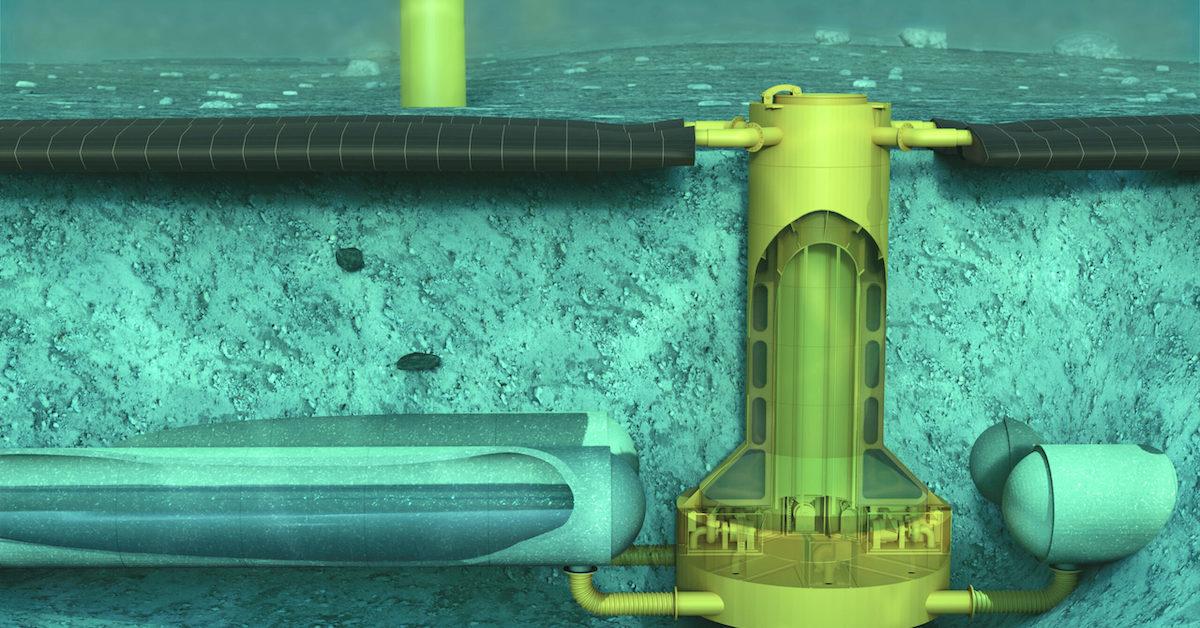
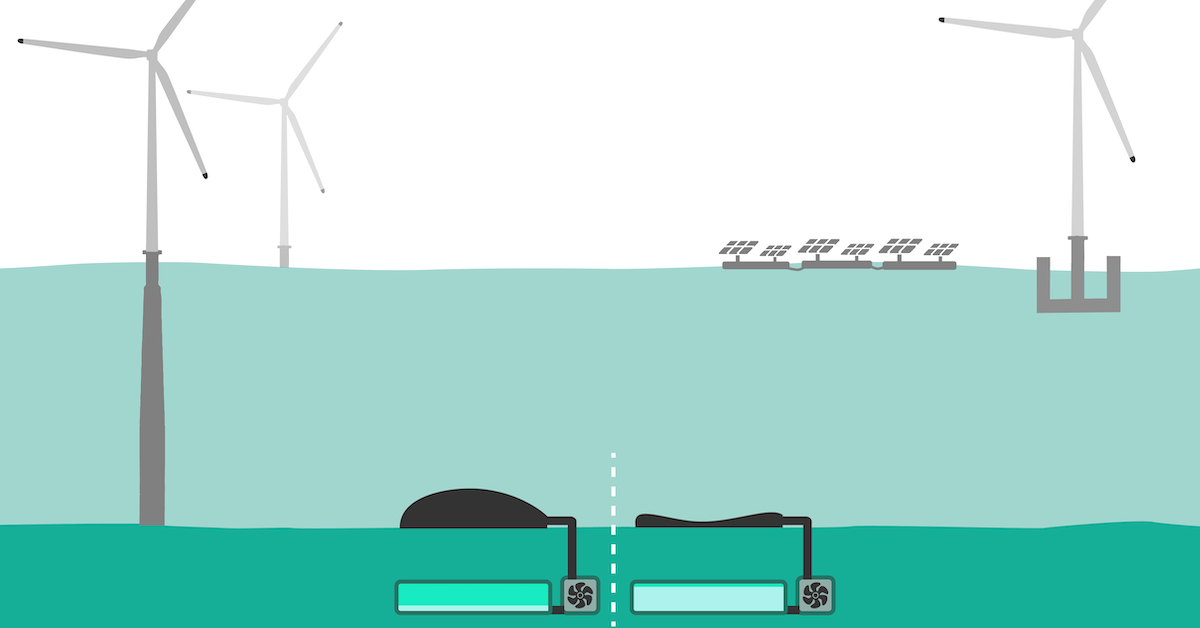
As previously mentioned, the Ocean Battery is the brain child of a Dutch company called Ocean Grazer, which is made up of a group of water engineers from the Netherlands' University of Groningen. It's designed to sit on the ocean floor within close proximity to offshore wind turbines or floating solar energy farms, effectively storing renewable energy for days when the sun doesn't shine or the wind doesn't blow. New Atlas explains that it functions somewhat similarly to a hydroelectric dam.
Basically, a "reservoir" of about 5.3 million gallons of fresh water will be buried beneath the ocean floor. Water will pump into a "bladder" when energy from the wind or solar farm is being sent in for storage. Then, when locals grids are in need of energy, the bladder will release water back into the reservoir. It will then go through a series of turbines that spin and create electricity. With up to 80 percent efficiency, it should be able to operate limitlessly for more than 20 years.
According to Japan Today, Ocean Grazer will have an operational Ocean Battery in the northern Netherlands as early as 2023, with hopes for its expansion by 2025.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Ocean Battery?
The Ocean Battery could come in handy for several reasons. According to the press release, it's incredibly high-tech, but it's relatively flexible and scalable. It also makes the transition to renewable energy much easier — if weather conditions aren't ideal for solar or wind farms to obtain energy, it has some set aside in storage, without destabilizing the power grid.
Economically, solar and wind energy is much cheaper than crude oil, and other non-renewables. The environmental impact is also next to nothing.
According to Japan Today, the process of implementing this type of technology could take much longer than expected. And of course, drilling into the sea bed obviously come with some environmental impacts. However, it could be a good step towards the transition to clean energy, and to curbing climate change, as a whole.